Category: Power Wheelchair
Posted by 2025-12-30 10:12
hoyer lift hydraulic
A Comprehensive Analysis of Hoyer Lift Hydraulic Systems: The Core Technology Behind Smooth Lifting and Lowering
The hydraulic system is the "heart" of a manual Hoyer Lift. Leveraging precise hydrodynamics principles, it transforms heavy transfer tasks into smooth, controllable operations. Gaining a deep understanding of this system not only enhances operational efficiency but also ensures long-term reliable safety performance.
Working Principles of the Hydraulic System
Basic Physical Principles
Pascal’s Law: Pressure applied to an incompressible fluid in a closed container is uniformly transmitted throughout the fluid.
Lever Effect: Amplifies force through the area difference between large and small pistons.
Energy Conversion: Converts mechanical energy from manual operation into hydraulic energy, which is then transformed into potential energy for lifting.
Composition of Core Components
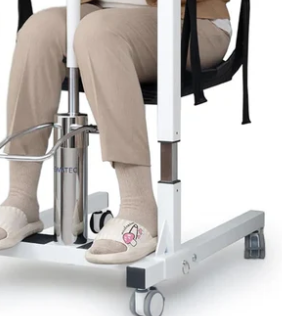
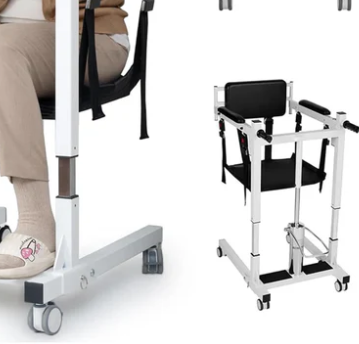
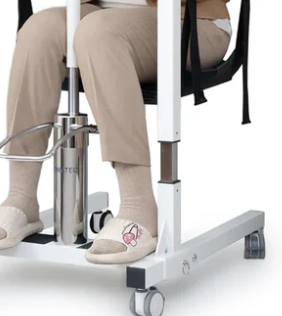
Main Hydraulic Cylinder: The primary chamber that houses the piston and hydraulic oil.
Manual Pump: Generates hydraulic pressure through handle operation.
Release Valve: A critical safety component that controls the lowering speed.
Oil Reservoir: A backup container for replenishing hydraulic oil.
Sealing System: Various O-rings and gaskets that prevent oil leakage.
Detailed Explanation of Operating Mechanisms
Lifting Process
Manual pumping of the handle generates initial pressure.
Hydraulic oil pushes the main piston upward.
A one-way valve prevents oil from flowing back, maintaining the lifted position.
Continuous pumping achieves smooth upward movement.
An internal safety valve prevents pressure from exceeding limits.
Lowering Control
Slowly rotate the release valve handle.
Control the flow rate of oil returning to the reservoir.
Gravity drives the piston downward.
Precise adjustment enables smooth lowering.
Quick, full release is possible in emergency situations.
Retention Mechanism
Precisely machined mating components ensure sealing performance.
High-quality hydraulic oil provides stable operation.
A specially designed valve system prevents unintended lowering.
Temperature compensation design adapts to environmental changes.
Professional Maintenance Guide
Key Points for Daily Inspection
Leakage Check: Inspect all connections for oil stains.
Operation Test: Verify smooth lifting/lowering with no abnormal noises.
Oil Level Check: Confirm the oil level is within the normal range via the sight glass.
Seal Evaluation: Inspect the integrity of all visible seals.
Regular Maintenance Schedule
Monthly: Thoroughly clean the exterior and check operational smoothness.
Quarterly: Conduct a detailed inspection of the sealing system and test load-bearing performance.
Annually: Professionally replace hydraulic oil and fully inspect the system’s sealing performance.
As Needed: Adjust the maintenance cycle based on usage frequency.
Hydraulic Oil Management
Type Selection: Strictly use the oil type recommended by the manufacturer.
Replacement Cycle: Typically every 2–3 years, or as determined by usage frequency.
Oil Inspection: Check the oil’s color, viscosity, and cleanliness.
Proper Disposal: Dispose of waste oil in compliance with environmental regulations.
Troubleshooting and Resolution
Analysis of Common Issues
Difficulty Lifting: Insufficient oil level, degraded oil quality, or air entering the system.
Unintended Lowering: hoyer lift hydraulic Worn seals or a faulty release valve.
Abnormal Noises: hoyer lift hydraulic Air trapped in the system or worn mechanical components.
Leakage Problems: Aging O-rings or loose connection parts.
On-Site Emergency Handling
Immediately stop using the faulty equipment.
Assess the severity of the issue and associated safety risks.
Implement appropriate temporary safety measures.
Contact professional technicians for repairs.
Document details of the problem for reference during repairs.
Preventive Measures
Establish records of regular maintenance.
Train operators to recognize early warning signs.
Maintain an inventory of spare parts to address sudden failures.
Build long-term partnerships with reliable service providers.
Safety Performance Features
Multi-Protection Design
Overload Protection: An internal safety valve prevents excessive pressure.
Emergency Lowering: A reliable manual release system for fault scenarios.
Gradual Control: Precise fine-tuning capability for lifting and lowering.
Fail-Safe Design: Redundancy concepts applied to critical components.
Safety Specifications for Use
Strictly adhere to the rated load capacity limits.
Avoid use in extreme temperature environments.
Prohibit the use of non-original hydraulic oil.
Conduct regular professional safety inspections.
Technological Upgrades and Innovations
Trends in Modern Improvements
Self-Venting Design: Reduces performance issues caused by air entry.
Temperature Adaptability: Wide-temperature-range hydraulic oil improves environmental suitability.
Sealing Technology: New materials extend service life.
Maintenance Alerts: Smart indicators remind users of maintenance needs.
User Experience Optimization
Ergonomic Handle: Operation design that conforms to human engineering principles.
Visible Oil Sight Glass: Enables quick and easy oil level checks.
Misoperation Prevention: Safety locking mechanism for the release valve.
Operational Feedback: Clear tactile and audio cues.
Comparison with Traditional Mechanical Systems
Advantages of Hydraulic Systems
Smoother lifting and lowering experience.
Precise fine-tuning control capability.
Higher force amplification efficiency.
Longer service life.
Application Scenario Analysis
Long-Term Care: Reliable performance for daily use.
Home Environments: Lower maintenance requirements.
Budget Considerations: More cost-effective solutions.
Technical Preferences: Traditional, mature mechanical principles.
Professional Purchasing Recommendations
Key Quality Evaluation Points
Sealing process quality of the hydraulic system.
Brand and specifications of the hydraulic oil used.
Material quality and machining precision of key components.
The manufacturer’s professional technical background.
Matching Usage Requirements
Evaluate daily usage frequency and intensity.
Consider the user’s weight range.
Analyze temperature conditions in the care environment.
Estimate the expected service life of the equipment.
Conclusion
The hydraulic system of a Hoyer Lift represents the perfect combination of mechanical precision and practical reliability. hoyer lift hydraulic This time-tested technical solution continues to provide indispensable care support for countless families and institutions. By deeply understanding its working principles, mastering correct maintenance methods, and following strict operational specifications, we can maximize the system’s performance and ensure every transfer is safe, smooth, and reliable. hoyer lift hydraulic When selecting and using a hydraulic Hoyer Lift, remember: careful maintenance and professional operation are the best guarantees for this "silent partner" to serve loyally for the long term.